Series 3 Version 4, 2 Winding Digital SG CIRCUIT ASSEMBLY
Series 3 Version 5, 2 Winding Digital SG CIRCUIT ASSEMBLY
Three events occur in the
Coils during a Spike hz Electron Pump's
Transient t2 Phase C when a
Switch #1's “t2 OFF” Impulse
influences an Electric and Magnetic Field.
A large VL
Spike may be created by the Reluctance of the Inductive Reactance (or
Inductance), where the magnitude of the
collapsing Electric and Magnetic Field is partially dependent on
Switch #1's "t2 OFF" Timing,
and the Impulse's expanding and
collapsing Electric and Magnetic Field is allowed to return its
accumulated non-Ghosted Electron Energy,
that has become greater than its
Source V, to
the Coils. This isolated
Current's Impulse Density Intensity Field,
caused by Switch #1's “t2 OFF,”
has been amplified by an
Impulse's VL
Spike's non-Ghosted Electrons and then captured within the Transient
Phase.
These t1 and
t2 Timing series' cycles (Transient
Phases B and C from Fig. 23) of
Switch #1's "t1 ON,"
in concert with the "shorted Coil's Electron building Transient
t1 Phase B until the
Electron Energy compressed equals
the target AVE DC,"
and Switch
#1's "t2 OFF", (or
Transient t2 Phase C), is
creating a VL
Spike along with Transient
t2 Phase's secondary t1,
introduced through the 1K tuning Resistor, follows
with another t2's expanding and collapsing Magnetic Field,
and this series and cycle ends
with Transient t3's Relaxation Phase.
(The secondary t1 and t2 are simply doubling the Mechanical version's
VL
Spike's frequency to increase the
AVE DC.)
All these Impulse events transpire in a
symphony of Magnetic Fields,
which both split the positives
and capture
all the Transient
Phases' Electric and Magnetic Fields' FREE Electron expansions and
collapses throughout each series of the cyclic process,
reaching beyond "Zero Point
Energy."
Each Transient Phases Coils'
series encapsulates the innate Electron response and Efficiency of
Tesla's design, and prepares Tinkerers for What We Now Know Beyond
Bedini Generators.
A Mechanical Three Winding SG Circuit

School Girl Oscillation's Chart
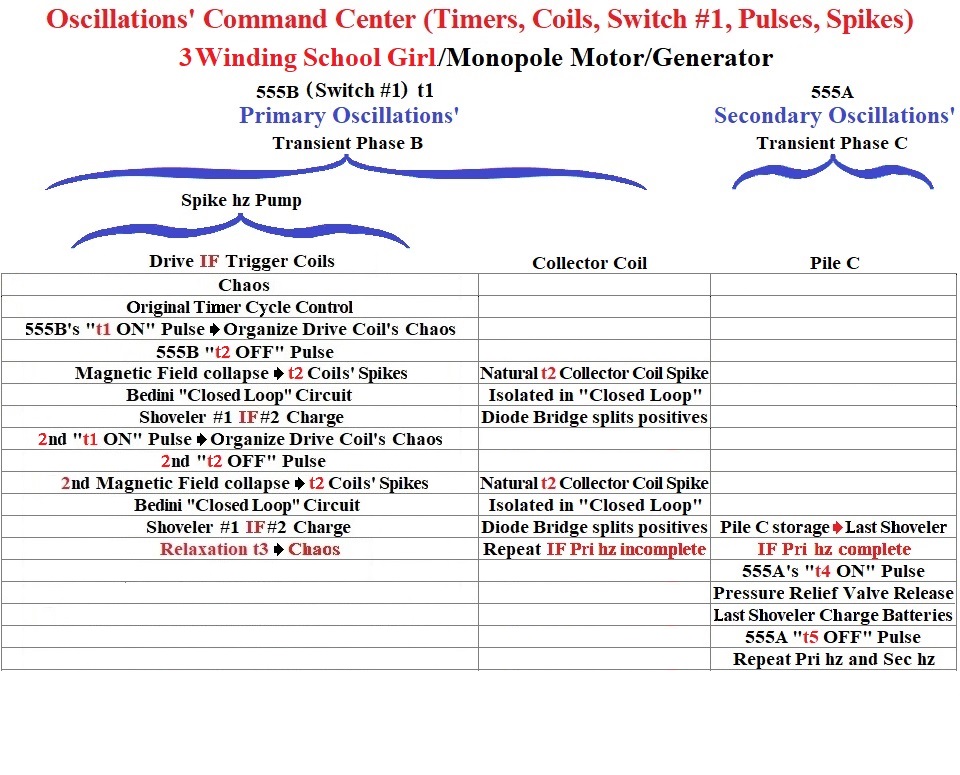
The “School Girl Oscillation's Chart” depicts a general visual for the characteristic design of Bedini's sequential stages, which create an increase in Electron Density Intensity Energy manifest as a Spike, and then isolate and capture that Electron Density Intensity Energy increase.
Series 3 Version 3, 3 Winding Mechanical SG CIRCUIT ASSEMBLY
Series 3 Version 4, 2 Winding Digital SG CIRCUIT ASSEMBLY
Series 3 Version 5, 2 Winding Digital SG CIRCUIT ASSEMBLY
Either any of my Transient Phase Simulations or the CircuitMaker Program are using Excel
(or Spreadsheet type tec hniques) for their intense calculations.
It is, therefore, advisable and wise to know Three things:
Any of these resources files can be corrupted if your
computer's resources are over-taxed.
and a requirement to use any of the Transient Phase Simulations is to have Excel or an equivalent.
Preserve Original File, and Work only from a backup to avoid File corruption when using these resources, and be vigilant protecting your work.
Return
Home